


|
ENERGY
|
GAIN ENERGY
APPRENTICE
LEVEL1
|
THE
ENERGY BLOCKAGE REMOVAL
PROCESS
|
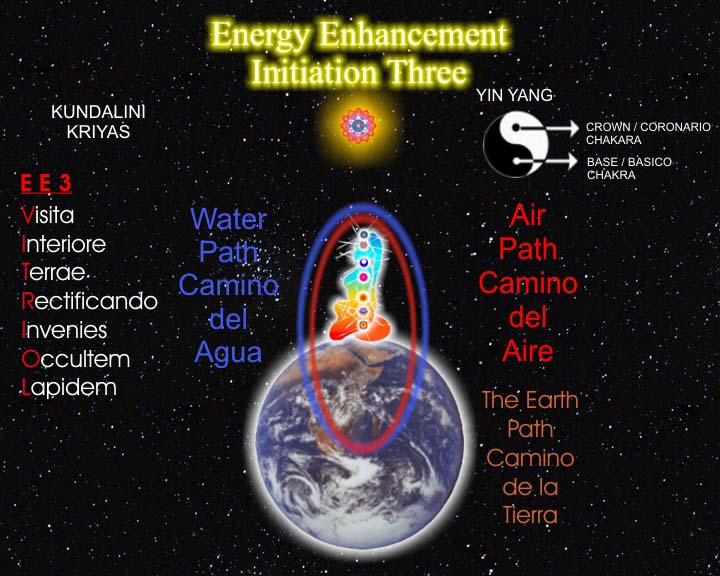
THE
KARMA CLEARING
PROCESS
APPRENTICE
LEVEL3
|
MASTERY
OF RELATIONSHIPS
TANTRA
APPRENTICE
LEVEL4
|
2005 AND 2006
|
|
Seeds of Light Information Service |
||||
|
Pesticides Use On The Food We Eat
Pesticides and Profit In order to keep profit margins high, factory farming routinely uses chemical pesticides to protect crops from insects and animals. Many good biological, nonchemical, and nontoxic methods are seldom used. The pesticide industry markets its products and vigorously promotes vast savings for growers. The dangers of pesticides have become well known in the industrialized countries. Many have banned the use of certain kinds, but these very same pesticides are still manufactured and exported to other countries. For example, one-quarter
of the pesticides exported by the U.S. companies cannot be sold in the
U.S. for any purpose (1). Ironically, agricultural products sprayed
with banned pesticides return to the U.S., which imports about 25% of
all the fruits and vegetables its population consumes.
Children are at special
risk. They have smaller bodies than adults and tend to eat more fresh
fruit and vegetables. Therefore they are exposed to a much higher concentration
of cancer-causing pesticides - about 4 times more than adults.
Pesticides facts and figures
Why Are Pesticides Different From Other Chemicals? Pesticides are released into the environment as toxic chemicals, intended to kill various insect, mammal, plant, and other pests.
Pesticides are used in enormous quantities
In
1986, it is established that over a billion gallons of pesticide spray
was used in Britain. In 1987, 26.5 million kg of active ingredients were
used in Britain alone, that works out at nearly a quarter of a pound of
active ingredient per head of population. This represents sales worth
over £409 million.
Pesticides Are Used Over A Huge Area Of Land In
1983, the estimated area of land treated each year with pesticides was
nearly 26 million acres. Many crops, especially fruit and vegetables,
are treated with multiple applications of pesticides.
People Have No Control Over Their Exposure Of Pesticides People may be exposed to pesticides through their work, in factories, farms, or parks. As well as occupational exposure, people may be unwittingly exposed by coming into contact with spray drift from adjacent field areas that have recently been treated, or through ingesting pesticide residues in food and water.
Alternatives to Pesticide Use After viewing the above data we can see that the mass use of pesticides and organophosphates is not only very damaging to human health and the environment, but is also not proving to be very effective in pest control. What alternatives are there to the agricultural use of pesticides?
IPM is a general
term that refers to an ecological or holistic approach to pest control.
It can include all forms of control used in such a way to maintain pest
populations below levels which cause economic injury, while minimising
hazards to humans and the environment. It therefore avoids unnecessary
or excessive blanket pesticide use.
IPM relies on an
understanding of all the components of a given agroecosystem. This would
include knowledge of the biology of the crops, pests, their natural enemies,
soil flora and fauna as well as abiotic factors such as the soil and climate.
The theoretical concept
of IPM is not new but the extent of its use in practice has been low.
Modern IPM was developed in the early 1950's, but traditional farmers
have practised many elements of IPM for centuries.
An IPM programme
attempts to maximise natural pest control and minimise the need for outside
measures such as the use of synthetic chemical pesticides. IPM can include
any of the following pest control methods.
Allows natural enemies which already exist in an area to be introduced, protected or augmented.
Requires the use of a combination of farming practices such as tillage, planting, irrigation, sanitation, mixed cropping and crop rotation which makes the environment less favourable for pests.
All
aspects of IPM involve the dissemination and proliferation of
information. IPM
works in a slow, gradual fashion, and educational resources are needed
to ensure successful and continued pest control.
IPM programmes allow for a reduction in pesticide use which reduces the risk of environmental and human damage. In the case of organic farming synthetic pesticides and soluble fertilizers are not used at all. Organic agriculture relies on a knowledge of ecology. It seeks to strive for a balance between crop production and environmental protection. The long term health of the soil is vital to the process of organic farming and much emphasis is placed on building soil fertility and maintaining a healthy soil profile.
Organic farming creates more jobs and produces better, life enhancing food. Although organic food production uses more land this is counterbalanced by the fact that about 20 vegetarians can be fed on the land that it takes to feed 1 meat eater. This astounding fact can be further supported by the following data. Eighty per cent of the corn raised in the United States is fed to livestock, as well as 95% of the oats. Altogether, 56% of all agricultural land in the United States is used for beef production.(4)
Organic farming requires
more care and attention, but the rewards are real and healthy food, and
a sustainable agricultural system that respects the earth.
References
|
||||
|
||||